“10 Shocking Causes of Knee Pain and Fixes”
10 Shocking Causes of Knee Pain and Effective Fixes
Discover 10 shocking causes of knee pain and learn effective solutions to relieve discomfort and regain mobility.
Introduction
Overview of Knee Pain and Its Impact on Daily Life
Knee pain is a common issue that affects people of all ages. Injuries, medical conditions, or gradual wear and tear can cause it. Knee pain can significantly impact daily life, making it difficult to perform routine activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and even sitting or standing for extended periods. The discomfort and limitations caused by knee pain can lead to a decreased quality of life and reduced mobility.
Brief Explanation of the Importance of Addressing Knee Pain
Addressing knee pain is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Ignoring knee pain can lead to further complications, including chronic pain, joint damage, and decreased mobility. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can help alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent long-term damage. It is essential to identify the underlying cause of knee pain and implement effective solutions to manage and reduce discomfort.
Cause 1: Osteoarthritis
Explanation of How Osteoarthritis Affects the Knee Joint
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that commonly affects the knee joint. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in the knee joint gradually wears away. This leads to bone-on-bone contact, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. Osteoarthritis can develop due to aging, repetitive stress on the knee joint, previous injuries, or genetic factors. The condition can significantly impact mobility and quality of life, making it challenging to perform everyday activities.
Effective Fixes for Osteoarthritis
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the stress on the knee joint and alleviate pain. Losing excess weight can help decrease the load on the knees, reducing the risk of further cartilage damage.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to address specific needs and limitations.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help manage pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or recommend corticosteroid injections to provide relief.
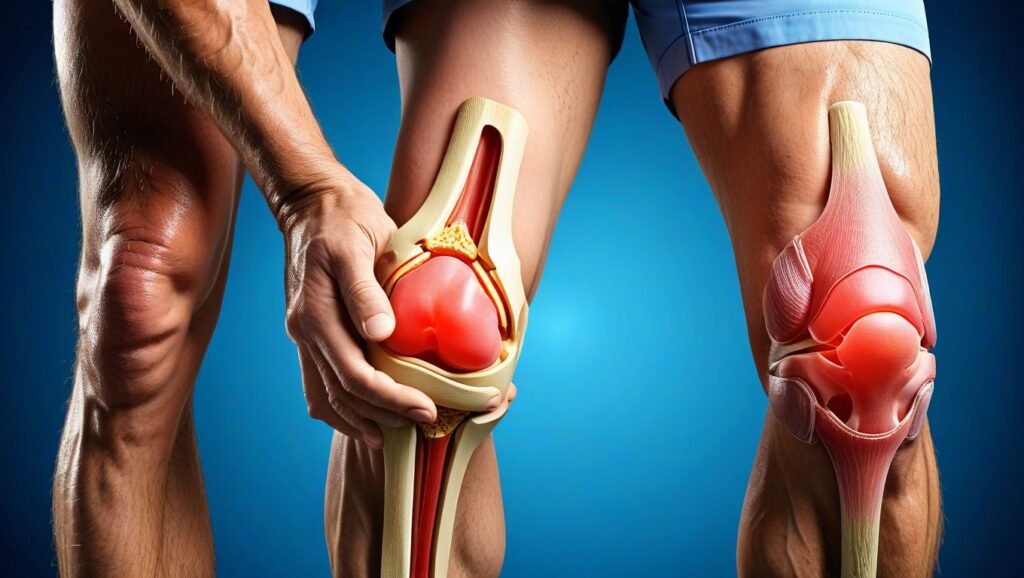
Cause 2: Rheumatoid Arthritis
How Rheumatoid Arthritis Leads to Knee Pain
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes the body’s immune system to attack the synovium, the lining of the membranes that surround the joints. This leads to inflammation, pain, and swelling in the affected joints, including the knees. Over time, the inflammation can cause damage to the cartilage and bones, leading to joint deformity and loss of function. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect people of all ages and often results in chronic pain and disability.
Effective Fixes for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Medications such as NSAIDs and corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic agents can also be prescribed to slow the progression of the disease and prevent joint damage.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint function, increase range of motion, and reduce pain. A physical therapist can develop an exercise program tailored to the individual’s needs, focusing on strengthening the muscles around the knee joint and improving flexibility.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress, can help manage rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming and cycling, can be beneficial for maintaining joint health without putting excessive stress on the knees.
By addressing the underlying causes of knee pain and implementing effective solutions, individuals can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and maintain mobility. If you experience persistent knee pain, it is essential to seek medical advice to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
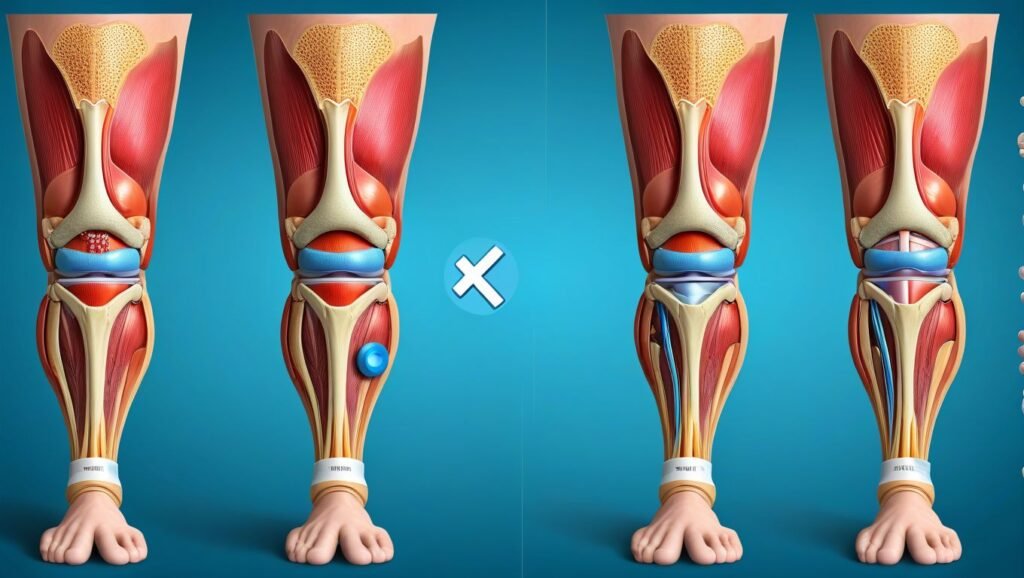
Cause 3: Meniscus Tears
Explanation of Meniscus Tears and Their Impact on Knee Function
The meniscus is a C-shaped piece of cartilage that acts as a cushion between the thigh bone (femur) and the shin bone (tibia). Each knee has two menisci—one on the inner side (medial meniscus) and one on the outer side (lateral meniscus). Meniscus tears are common knee injuries that can occur due to sudden twisting or turning movements, especially during sports activities. They can also result from degenerative changes in the knee joint as we age.
A meniscus tear can cause pain, swelling, stiffness, and a reduced range of motion. It may also lead to a sensation of the knee “locking” or “giving way.” The severity of the tear can vary, ranging from minor tears that may heal on their own to more severe tears that require medical intervention.
Effective Fixes for Meniscus Tears
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): The RICE method is a common initial treatment for meniscus tears. Resting the knee, applying ice to reduce swelling, using compression bandages, and elevating the leg can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and restore function. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to aid in recovery.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
- Surgery: In cases of severe meniscus tears that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgery may be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery is a minimally invasive procedure that can repair or remove the damaged portion of the meniscus.
Cause 4: Ligament Injuries
How Ligament Injuries, Such as ACL Tears, Cause Knee Pain
Ligament injuries are common causes of knee pain, particularly injuries to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The ACL is one of the four major ligaments in the knee that helps stabilize the joint. ACL tears often occur during activities that involve sudden stops, changes in direction, or jumping, such as in sports like soccer, basketball, and skiing.
An ACL tear can cause immediate pain, swelling, and a feeling of instability in the knee. The knee may also “give out” during physical activity. Other ligaments in the knee, such as the medial collateral ligament (MCL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), can also be injured, leading to similar symptoms.
Effective Fixes for Ligament Injuries
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is a crucial component of recovery for ligament injuries. A physical therapist can develop a rehabilitation program to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve stability, and restore range of motion. Exercises may include strengthening, balance, and agility training.
- Bracing: Wearing a knee brace can provide additional support and stability to the injured ligament. Braces can help prevent further injury and allow for safer participation in physical activities.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe ligament injuries, such as complete ACL tears, surgery may be necessary to reconstruct the damaged ligament. ACL reconstruction surgery involves replacing the torn ligament with a graft, which can be taken from the patient’s own tissue or a donor. Post-surgery rehabilitation is essential for a successful recovery.
By addressing the underlying causes of knee pain and implementing effective solutions, individuals can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and maintain mobility. If you experience persistent knee pain, it is essential to seek medical advice to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Cause 5: Patellar Tendinitis
Explanation of Patellar Tendinitis and Its Symptoms
Patellar tendinitis, also known as jumper’s knee, is an overuse injury that affects the patellar tendon, which connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia). This condition is common among athletes who engage in sports that involve frequent jumping, such as basketball and volleyball. Patellar tendinitis occurs when the patellar tendon becomes inflamed and irritated due to repetitive stress and strain.
Symptoms of patellar tendinitis include:
- Pain and tenderness around the patellar tendon, especially during physical activity
- Swelling and inflammation in the knee area
- Stiffness and difficulty bending or straightening the knee
- Weakness in the affected leg
Effective Fixes for Patellar Tendinitis
- Rest: Resting the knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is crucial for allowing the tendon to heal. Taking a break from high-impact sports and activities can help reduce inflammation and prevent further injury.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Ice packs should be applied for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and reduce stress on the patellar tendon. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program that includes stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises that target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves muscles can help support the knee joint and reduce the risk of future injuries. Eccentric exercises, which involve lengthening the muscle while it is under tension, are particularly effective for treating patellar tendinitis.
Cause 6: Bursitis
How Bursitis Leads to Knee Pain and Inflammation
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles. In the knee, bursitis commonly affects the prepatellar bursa, located in front of the kneecap, or the pes anserine bursa, located on the inner side of the knee. Bursitis can result from repetitive kneeling, direct trauma to the knee, or underlying conditions such as arthritis.
Symptoms of bursitis include:
- Pain and tenderness around the affected bursa
- Swelling and warmth in the knee area
- Limited range of motion and stiffness
- Redness and inflammation
Effective Fixes for Bursitis
- Rest: Resting the knee and avoiding activities that put pressure on the affected bursa is essential for reducing inflammation and allowing the bursa to heal. Taking breaks from activities that involve prolonged kneeling or repetitive movements can help prevent further irritation.
- Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain. Ice packs should be applied for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases, doctors may prescribe stronger medications or recommend corticosteroid injections to provide relief.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve joint function, increase range of motion, and reduce pain. A physical therapist can develop an exercise program tailored to the individual’s needs, focusing on strengthening the muscles around the knee and improving flexibility.
By addressing the underlying causes of knee pain and implementing effective solutions, individuals can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and maintain mobility. If you experience persistent knee pain, it is essential to seek medical advice to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Cause 7: Gout
Explanation of How Gout Affects the Knee Joint
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a waste product that forms when the body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods and drinks. When uric acid levels in the blood become too high, it can form sharp, needle-like crystals that deposit in the joints, leading to intense pain, swelling, and inflammation. The knee joint is one of the common sites affected by gout.
Symptoms of gout in the knee include:
- Sudden and severe pain, often occurring at night
- Swelling and redness around the knee joint
- Warmth and tenderness in the affected area
- Limited range of motion due to pain and swelling
Effective Fixes for Gout
- Dietary Changes: Making dietary changes can help reduce uric acid levels and prevent gout flare-ups. Avoiding foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, shellfish, and certain types of fish, can be beneficial. Increasing the intake of low-purine foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products, can also help. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water can aid in flushing out excess uric acid from the body.
- Medications: Medications can help manage gout symptoms and prevent future attacks. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, and colchicine can be used to reduce pain and inflammation during a gout flare-up. Long-term medications such as allopurinol and febuxostat can help lower uric acid levels and prevent future attacks.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage gout and reduce the risk of flare-ups. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can be beneficial. Managing stress and getting adequate sleep can also help prevent gout attacks.
Cause 8: Overuse Injuries
How Repetitive Stress and Overuse Lead to Knee Pain
Overuse injuries occur when repetitive stress and strain are placed on the knee joint, leading to inflammation, pain, and damage to the tissues. These injuries are common among athletes and individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive movements, such as running, cycling, and jumping. Overuse injuries can affect various structures in the knee, including the tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
Symptoms of overuse injuries include:
- Gradual onset of pain that worsens with activity
- Swelling and tenderness around the knee joint
- Stiffness and limited range of motion
- Weakness in the affected leg
Effective Fixes for Overuse Injuries
- Rest: Resting the knee and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is crucial for allowing the tissues to heal. Taking breaks from high-impact sports and activities can help reduce inflammation and prevent further injury.
- Activity Modification: Modifying activities to reduce stress on the knee joint can help prevent overuse injuries. This may involve changing the intensity, duration, or frequency of activities, as well as incorporating low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, into the routine.
- Strengthening Exercises: Specific exercises that target the muscles around the knee can help support the joint and reduce the risk of future injuries. Strengthening the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles can improve stability and reduce stress on the knee. A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to aid in recovery and prevent recurrence.
By addressing the underlying causes of knee pain and implementing effective solutions, individuals can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and maintain mobility. If you experience persistent knee pain, it is essential to seek medical advice to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Cause 9: Infections
Explanation of Knee Joint Infections and Their Symptoms
Knee joint infections, also known as septic arthritis, occur when bacteria or other pathogens invade the knee joint, leading to inflammation and pain. This condition can result from an infection elsewhere in the body that spreads to the knee joint through the bloodstream or from a direct injury to the knee that introduces bacteria. Common bacteria that cause knee joint infections include Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species.
Symptoms of knee joint infections include:
- Severe pain in the knee joint
- Swelling and redness around the knee
- Warmth and tenderness in the affected area
- Fever and chills
- Limited range of motion due to pain and swelling
Effective Fixes for Knee Joint Infections
- Antibiotics: Prompt treatment with antibiotics is essential to eliminate the infection and prevent further damage to the knee joint. The choice of antibiotics depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection. Intravenous (IV) antibiotics may be required initially, followed by oral antibiotics.
- Drainage: In some cases, drainage of the infected joint fluid may be necessary to remove pus and reduce inflammation. This can be done through needle aspiration or surgical drainage.
- Surgical Intervention: If the infection is severe or does not respond to antibiotics and drainage, surgical intervention may be needed. This can involve arthroscopic surgery to clean out the infected joint or open surgery in more severe cases.
Cause 10: Obesity
How Excess Weight Contributes to Knee Pain and Joint Stress
Obesity is a significant risk factor for knee pain and joint stress. Excess weight places additional pressure on the knee joints, leading to increased wear and tear on the cartilage and other structures. This can result in conditions such as osteoarthritis, where the cartilage that cushions the knee joint gradually wears away, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. Obesity can also contribute to inflammation in the body, further exacerbating knee pain.
Effective Fixes for Obesity-Related Knee Pain
- Weight Loss: Losing excess weight can significantly reduce the stress on the knee joints and alleviate pain. A combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve joint stability, and reduce pain. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming, cycling, and walking, are particularly beneficial for individuals with knee pain.
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support weight loss and overall health. Reduced intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods can also help manage weight and reduce inflammation.
Conclusion
Recap of the 10 Shocking Causes of Knee Pain and Their Effective Fixes
- Osteoarthritis: Weight management, physical therapy, and medications
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes
- Meniscus Tears: Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), and surgery if necessary
- Ligament Injuries: Physical therapy, bracing, and surgical intervention
- Patellar Tendinitis: Rest, ice, physical therapy, and strengthening exercises
- Bursitis: Rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy
- Gout: Dietary changes, medications, and lifestyle modifications
- Overuse Injuries: Rest, activity modification, and strengthening exercises
- Infections: Antibiotics, drainage, and surgical intervention if needed
- Obesity: Weight loss, exercise, and dietary changes
Encouragement to Seek Medical Advice if Experiencing Knee Pain
If you experience persistent knee pain, it is essential to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent long-term damage to the knee joint.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of Maintaining Knee Health
Maintaining knee health is crucial for overall well-being and mobility. By addressing the underlying causes of knee pain and implementing effective solutions, individuals can manage their symptoms, improve their quality of life, and maintain an active lifestyle. Prioritizing a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management can help protect the knee joints and prevent future issues.
If you experience persistent knee pain, seek medical advice to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Early intervention can alleviate pain, improve function, and prevent long-term damage. Maintaining knee health is crucial for overall well-being and mobility. By addressing underlying causes and implementing effective solutions, individuals can manage symptoms, improve their quality of life, and maintain an active lifestyle. Prioritizing a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management can protect the knee joints and prevent future issues.


Post Comment